|
POTASSIUM OXALATE MONOHYDRATE
| ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 583-52-8
(Anhydrous) 6487-48-5 (Monohydrate) 127-96-8 (Dihydrate) |
|
| EINECS NO. |
209-506-8 (Anhydrous) 204-874-6 (Dihydrate) | |
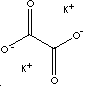
| FORMULA | K2C2O4·H2O | |
| MOL WT. | 184.21 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2917.11.0000 | |
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Oxalic acid dipotassium salt monohydrate; | |
| Potassium oxalate monohydrate; Dikaliumoxalat (German); Oxalato de dipotasio (Spanish); Oxalate de dipotassium (French); Dipotassium oxalate monohydrate; | ||
| SMILES | O.[K+].[K+].[O-]C(=O)C([O-])=O | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Biological Buffer, Chelating agent | |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white crystals | |
| MELTING POINT | 356 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 2.13 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 364 g/l at 20 C | |
| pH | 7- 8 | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 3; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
| REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Moisture sensitive | |
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||
|
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Potassium oxalate PubChem Compound Summary - Potassium oxalate Local: |
||
|
|
||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystals | |
| PURITY | 99.0% min | |
|
CHLORIDE |
0.01% max | |
|
SULFATE |
0.01% max | |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max | |
|
IRON |
10ppm max | |
|
INSOLUBLES |
0.05% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 2811 | |
| SAFETY INFORMATION | ||
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Harmful if absorbed through the skin. Hygroscopic (absorbs moisture from the air). Harmful if swallowed. May cause kidney damage. Causes eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. Target Organs: Kidneys, heart, eyes, skin, brain, nerves, mucous membranes. |
|
|
GHS |
|
|
| SIGNAL WORD | Warning | |
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H312 Harmful in contact with skin |
|
|
PRECAUTIONARY STATEMENTS |
P280 Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face
protection |
|
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
21/22 Harmful in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
24/25: Avoid contact with skin and eyes |
|
|
PRICE INFORMATION |
||
|
|
||